本篇博客通过旭日X3搭载手势识别算法,实现实时检测,同时测试其运行性能。针对旭日X3上并没有很好的python IDE编译环境的问题,本篇博客通过SSH远程连接的方式,可以在不给旭日X3内存压力的同时, 提供一个更好的代码编写环境, 同时通过SSH的方式给旭日X3配置对应的环境 ,起到方便快捷的作用。
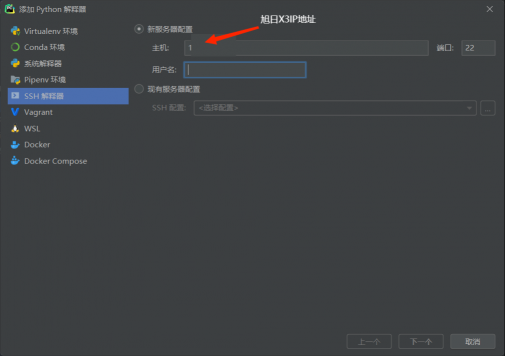
一.准备工作 首先在电脑上安装配有pycharm专业版(专业版可以使用ssh远程登陆,学生使用教育邮箱申请pycharm专业版)。Pycharm是一款用于Python编程的集成开发环境(IDE)。它可以帮助您编写,测试和调试代码,并具有诸如代码提示,自动完成和错误检测等功能,以帮助您更快地编写高质量的代码。本次主要使用通过SSH远程连接旭日X3,以便于传输代码到x3派上,实现python的远程操作。
其次,本次工作用到Meidapipe功能包,MediaPipe 是一款由 Google Research 开发并开源的多媒体机器学习模型应用框架,可以直接调用其API完成目标检测、人脸检测以及关键点检测等。Meidapipe是一个针对深度学习模型的高效执行库,由PyTorch设计而成,提供了高级API,用于加速预测和推理的过程。它为模型执行提供了优化和并行化的功能,并且支持多个GPU和分布式训练。同时,Meidapipe还支持模型压缩和部署,使模型在嵌入式设备和移动设备上的执行更加高效和灵活。
项目完成的效果展示:
二:部署过程 在x3派上安装pip3及导入Meidapipe包: sudo apt install python3-pip
sudo apt install python3-pip
复制
sudo apt install python3-pip制
pip3 install mediapipe -i https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/pypi/simple
pip3 install mediapipe -i https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/pypi/simple
复制
pip3 install mediapipe -i https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/pypi/simple
确定旭日X3中摄像头端口: 首先不插usb摄像头输入
ls /dev/video*
复制 ls /dev/video*
ls /dev/video*
然后插上usb摄像头再输入ls /dev/video*
ls /dev/video*
复制
ls /dev/video*
ls /dev/video*
多出的端口号即为摄像头端口。
创建手部类对象 初始化手部对象
hands是检测手部关键点的函数,其中有4个输入参数量可以选择
1、static_image_mode:默认为False,如果设置为false, 就是把输入看作一个视频流,在检测到手之后对手加了一个目标跟踪(目标检测+跟踪),无需调用另一次检测,直到失去对任何手的跟踪为止。如果设置为True,则手部检测将在每个输入图像上运行(目标检测),非常适合处理一批静态的,可能不相关的图像。(如果检测的是图片就要设置成True)
2、max_num_hands:可以检测到的手的数量最大值,默认是2
3、min_detection_confidence: 手部检测的最小置信度值,大于这个数值被认为是成功的检测。默认为0.5
4、min_tracking_confidence:目标踪模型的最小置信度值,大于这个数值将被视为已成功跟踪的手部,默认为0.5,如果static_image_mode设置为true,则忽略此操作。
class HandDetector:
"""
使用mediapipe库查找手。导出地标像素格式。添加了额外的功能。
如查找方式,许多手指向上或两个手指之间的距离。而且提供找到的手的边界框信息。
"""
def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, minTrackCon=0.5):
"""
:param mode: 在静态模式下,对每个图像进行检测
:param maxHands: 要检测的最大手数
:param detectionCon: 最小检测置信度
:param minTrackCon: 最小跟踪置信度
"""
self.mode = mode
self.maxHands = maxHands
self.modelComplex = False
self.detectionCon = detectionCon
self.minTrackCon = minTrackCon
# 初始化手部识别模型
self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands
self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(self.mode, self.maxHands, self.modelComplex,
self.detectionCon, self.minTrackCon)
self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils # 初始化绘图器
self.tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20] # 指尖列表
self.fingers = []
self.lmList = []class HandDetector: """ 使用mediapipe库查找手。导出地标像素格式。添加了额外的功能。 如查找方式,许多手指向上或两个手指之间的距离。而且提供找到的手的边界框信息。 """ def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, minTrackCon=0.5): """ :param mode: 在静态模式下,对每个图像进行检测 :param maxHands: 要检测的最大手数 :param detectionCon: 最小检测置信度 :param minTrackCon: 最小跟踪置信度 """ self.mode = mode self.maxHands = maxHands self.modelComplex = False self.detectionCon = detectionCon self.minTrackCon = minTrackCon # 初始化手部识别模型 self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(self.mode, self.maxHands, self.modelComplex, self.detectionCon, self.minTrackCon) self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils # 初始化绘图器 self.tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20] # 指尖列表 self.fingers = [] self.lmList = []
复制class HandDetector: """ 使用mediapipe库查找手。导出地标像素格式。添加了额外的功能。 如查找方式,许多手指向上或两个手指之间的距离。而且提供找到的手的边界框信息。 """ def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, minTrackCon=0.5): """ :param mode: 在静态模式下,对每个图像进行检测 :param maxHands: 要检测的最大手数 :param detectionCon: 最小检测置信度 :param minTrackCon: 最小跟踪置信度 """ self.mode = mode self.maxHands = maxHands self.modelComplex = False self.detectionCon = detectionCon self.minTrackCon = minTrackCon # 初始化手部识别模型 self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(self.mode, self.maxHands, self.modelComplex, self.detectionCon, self.minTrackCon) self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils # 初始化绘图器 self.tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20] # 指尖列表 self.fingers = [] self.lmList = []
class HandDetector: """ 使用mediapipe库查找手。导出地标像素格式。添加了额外的功能。 如查找方式,许多手指向上或两个手指之间的距离。而且提供找到的手的边界框信息。 """ def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, minTrackCon=0.5): """ :param mode: 在静态模式下,对每个图像进行检测 :param maxHands: 要检测的最大手数 :param detectionCon: 最小检测置信度 :param minTrackCon: 最小跟踪置信度 """ self.mode = mode self.maxHands = maxHands self.modelComplex = False self.detectionCon = detectionCon self.minTrackCon = minTrackCon # 初始化手部识别模型 self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(self.mode, self.maxHands, self.modelComplex, self.detectionCon, self.minTrackCon) self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils # 初始化绘图器 self.tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20] # 指尖列表 self.fingers = [] self.lmList = []
class HandDetector: """ 使用mediapipe库查找手。导出地标像素格式。添加了额外的功能。 如查找方式,许多手指向上或两个手指之间的距离。而且提供找到的手的边界框信息。 """ def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, minTrackCon=0.5): """ :param mode: 在静态模式下,对每个图像进行检测 :param maxHands: 要检测的最大手数 :param detectionCon: 最小检测置信度 :param minTrackCon: 最小跟踪置信度 """ self.mode = mode self.maxHands = maxHands self.modelComplex = False self.detectionCon = detectionCon self.minTrackCon = minTrackCon # 初始化手部识别模型 self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(self.mode, self.maxHands, self.modelComplex, self.detectionCon, self.minTrackCon) self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils # 初始化绘图器 self.tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20] # 指尖列表 self.fingers = [] self.lmList = []
创建发现手部并在图像中绘制函数,返回绘制后的图像。
def findHands(self, img, draw=True):
"""
从图像(BRG)中找到手部。
:param img: 用于查找手的图像。
:param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。
:return: 带或不带图形的图像
"""
imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 将传入的图像由BGR模式转标准的Opencv模式——RGB模式,
self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB)
if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
if draw:
self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms,
self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS)
return imgdef findHands(self, img, draw=True): """ 从图像(BRG)中找到手部。 :param img: 用于查找手的图像。 :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。 :return: 带或不带图形的图像 """ imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 将传入的图像由BGR模式转标准的Opencv模式——RGB模式, self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB) if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if draw: self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms, self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS) return img
复制def findHands(self, img, draw=True): """ 从图像(BRG)中找到手部。 :param img: 用于查找手的图像。 :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。 :return: 带或不带图形的图像 """ imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 将传入的图像由BGR模式转标准的Opencv模式——RGB模式, self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB) if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if draw: self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms, self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS) return img
def findHands(self, img, draw=True): """ 从图像(BRG)中找到手部。 :param img: 用于查找手的图像。 :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。 :return: 带或不带图形的图像 """ imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 将传入的图像由BGR模式转标准的Opencv模式——RGB模式, self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB) if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if draw: self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms, self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS) return img
复制
def findHands(self, img, draw=True): """ 从图像(BRG)中找到手部。 :param img: 用于查找手的图像。 :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。 :return: 带或不带图形的图像 """ imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 将传入的图像由BGR模式转标准的Opencv模式——RGB模式, self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB) if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if draw: self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms, self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS) return img
创建发现手部坐标函数,并返回手部坐标列表。
def findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True):
"""
查找单手的地标并将其放入列表中像素格式。还可以返回手部周围的边界框。
:param img: 要查找的主图像
:param handNo: 如果检测到多只手,则为手部id
:param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。(默认绘制矩形框)
:return: 像素格式的手部关节位置列表;手部边界框
"""
xList = []
yList = []
bbox = []
bboxInfo = []
self.lmList = []
if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo]
for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark):
h, w, c = img.shape
px, py = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h)
xList.append(px)
yList.append(py)
self.lmList.append([px, py])
if draw:
cv2.circle(img, (px, py), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
xmin, xmax = min(xList), max(xList)
ymin, ymax = min(yList), max(yList)
boxW, boxH = xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin
bbox = xmin, ymin, boxW, boxH
cx, cy = bbox[0] + (bbox[2] // 2), \
bbox[1] + (bbox[3] // 2)
bboxInfo = {"id": id, "bbox": bbox, "center": (cx, cy)}
if draw:
cv2.rectangle(img, (bbox[0] - 20, bbox[1] - 20),
(bbox[0] + bbox[2] + 20, bbox[1] + bbox[3] + 20),
(0, 255, 0), 2)
return self.lmList, bboxInfodef findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True): """ 查找单手的地标并将其放入列表中像素格式。还可以返回手部周围的边界框。 :param img: 要查找的主图像 :param handNo: 如果检测到多只手,则为手部id :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。(默认绘制矩形框) :return: 像素格式的手部关节位置列表;手部边界框 """ xList = [] yList = [] bbox = [] bboxInfo = [] self.lmList = [] if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo] for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark): h, w, c = img.shape px, py = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h) xList.append(px) yList.append(py) self.lmList.append([px, py]) if draw: cv2.circle(img, (px, py), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) xmin, xmax = min(xList), max(xList) ymin, ymax = min(yList), max(yList) boxW, boxH = xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin bbox = xmin, ymin, boxW, boxH cx, cy = bbox[0] + (bbox[2] // 2), \ bbox[1] + (bbox[3] // 2) bboxInfo = {"id": id, "bbox": bbox, "center": (cx, cy)} if draw: cv2.rectangle(img, (bbox[0] - 20, bbox[1] - 20), (bbox[0] + bbox[2] + 20, bbox[1] + bbox[3] + 20), (0, 255, 0), 2) return self.lmList, bboxInfo
复制def findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True): """ 查找单手的地标并将其放入列表中像素格式。还可以返回手部周围的边界框。 :param img: 要查找的主图像 :param handNo: 如果检测到多只手,则为手部id :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。(默认绘制矩形框) :return: 像素格式的手部关节位置列表;手部边界框 """ xList = [] yList = [] bbox = [] bboxInfo = [] self.lmList = [] if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo] for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark): h, w, c = img.shape px, py = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h) xList.append(px) yList.append(py) self.lmList.append([px, py]) if draw: cv2.circle(img, (px, py), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) xmin, xmax = min(xList), max(xList) ymin, ymax = min(yList), max(yList) boxW, boxH = xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin bbox = xmin, ymin, boxW, boxH cx, cy = bbox[0] + (bbox[2] // 2), \ bbox[1] + (bbox[3] // 2) bboxInfo = {"id": id, "bbox": bbox, "center": (cx, cy)} if draw: cv2.rectangle(img, (bbox[0] - 20, bbox[1] - 20), (bbox[0] + bbox[2] + 20, bbox[1] + bbox[3] + 20), (0, 255, 0), 2) return self.lmList, bboxInfo
def findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True): """ 查找单手的地标并将其放入列表中像素格式。还可以返回手部周围的边界框。 :param img: 要查找的主图像 :param handNo: 如果检测到多只手,则为手部id :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。(默认绘制矩形框) :return: 像素格式的手部关节位置列表;手部边界框 """ xList = [] yList = [] bbox = [] bboxInfo = [] self.lmList = [] if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo] for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark): h, w, c = img.shape px, py = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h) xList.append(px) yList.append(py) self.lmList.append([px, py]) if draw: cv2.circle(img, (px, py), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) xmin, xmax = min(xList), max(xList) ymin, ymax = min(yList), max(yList) boxW, boxH = xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin bbox = xmin, ymin, boxW, boxH cx, cy = bbox[0] + (bbox[2] // 2), \ bbox[1] + (bbox[3] // 2) bboxInfo = {"id": id, "bbox": bbox, "center": (cx, cy)} if draw: cv2.rectangle(img, (bbox[0] - 20, bbox[1] - 20), (bbox[0] + bbox[2] + 20, bbox[1] + bbox[3] + 20), (0, 255, 0), 2) return self.lmList, bboxInfo
复制
def findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True): """ 查找单手的地标并将其放入列表中像素格式。还可以返回手部周围的边界框。 :param img: 要查找的主图像 :param handNo: 如果检测到多只手,则为手部id :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。(默认绘制矩形框) :return: 像素格式的手部关节位置列表;手部边界框 """ xList = [] yList = [] bbox = [] bboxInfo = [] self.lmList = [] if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo] for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark): h, w, c = img.shape px, py = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h) xList.append(px) yList.append(py) self.lmList.append([px, py]) if draw: cv2.circle(img, (px, py), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) xmin, xmax = min(xList), max(xList) ymin, ymax = min(yList), max(yList) boxW, boxH = xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin bbox = xmin, ymin, boxW, boxH cx, cy = bbox[0] + (bbox[2] // 2), \ bbox[1] + (bbox[3] // 2) bboxInfo = {"id": id, "bbox": bbox, "center": (cx, cy)} if draw: cv2.rectangle(img, (bbox[0] - 20, bbox[1] - 20), (bbox[0] + bbox[2] + 20, bbox[1] + bbox[3] + 20), (0, 255, 0), 2) return self.lmList, bboxInfo
判断展开手指数量,同时区分左右手。
def fingersUp(self):
"""
查找列表中打开并返回的手指数。会分别考虑左手和右手
:return:竖起手指的列表
"""
if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
myHandType = self.handType()
fingers = []
# Thumb
if myHandType == "Right":
if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] > self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]:
fingers.append(1)
else:
fingers.append(0)
else:
if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]:
fingers.append(1)
else:
fingers.append(0)
# 4 Fingers
for id in range(1, 5):
if self.lmList[self.tipIds[id]][1] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[id] - 2][1]:
fingers.append(1)
else:
fingers.append(0)
return fingersdef fingersUp(self): """ 查找列表中打开并返回的手指数。会分别考虑左手和右手 :return:竖起手指的列表 """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHandType = self.handType() fingers = [] # Thumb if myHandType == "Right": if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] > self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) else: if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) # 4 Fingers for id in range(1, 5): if self.lmList[self.tipIds[id]][1] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[id] - 2][1]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) return fingers
复制def fingersUp(self): """ 查找列表中打开并返回的手指数。会分别考虑左手和右手 :return:竖起手指的列表 """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHandType = self.handType() fingers = [] # Thumb if myHandType == "Right": if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] > self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) else: if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) # 4 Fingers for id in range(1, 5): if self.lmList[self.tipIds[id]][1] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[id] - 2][1]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) return fingers
def fingersUp(self): """ 查找列表中打开并返回的手指数。会分别考虑左手和右手 :return:竖起手指的列表 """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHandType = self.handType() fingers = [] # Thumb if myHandType == "Right": if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] > self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) else: if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) # 4 Fingers for id in range(1, 5): if self.lmList[self.tipIds[id]][1] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[id] - 2][1]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) return fingers
复制
def fingersUp(self): """ 查找列表中打开并返回的手指数。会分别考虑左手和右手 :return:竖起手指的列表 """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHandType = self.handType() fingers = [] # Thumb if myHandType == "Right": if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] > self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) else: if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) # 4 Fingers for id in range(1, 5): if self.lmList[self.tipIds[id]][1] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[id] - 2][1]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) return fingers
判断识别到的是左手 or 右手。
def handType(self):
"""
检查传入的手部是左还是右
:return: "Right" 或 "Left"
"""
if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
if self.lmList[17][0] < self.lmList[5][0]:
return "Right"
else:
return "Left"def handType(self): """ 检查传入的手部是左还是右 :return: "Right" 或 "Left" """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if self.lmList[17][0] < self.lmList[5][0]: return "Right" else: return "Left"
复制def handType(self): """ 检查传入的手部是左还是右 :return: "Right" 或 "Left" """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if self.lmList[17][0] < self.lmList[5][0]: return "Right" else: return "Left"
def handType(self): """ 检查传入的手部是左还是右 :return: "Right" 或 "Left" """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if self.lmList[17][0] < self.lmList[5][0]: return "Right" else: return "Left"
复制
def handType(self): """ 检查传入的手部是左还是右 :return: "Right" 或 "Left" """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if self.lmList[17][0] < self.lmList[5][0]: return "Right" else: return "Left"
以上为手部检测类中方法的创建实现,通过调用类的方式来实现相应的功能。
创建Main类,用于具体实现功能 摄像头初始化
class Main:
def __init__(self):
self.camera = cv2.VideoCapture(1, cv2.CAP_DSHOW)
self.camera.set(3, 1280)
self.camera.set(4, 720)class Main: def __init__(self): self.camera = cv2.VideoCapture(1, cv2.CAP_DSHOW) self.camera.set(3, 1280) self.camera.set(4, 720)
复制class Main: def __init__(self): self.camera = cv2.VideoCapture(1, cv2.CAP_DSHOW) self.camera.set(3, 1280) self.camera.set(4, 720)
class Main: def __init__(self): self.camera = cv2.VideoCapture(1, cv2.CAP_DSHOW) self.camera.set(3, 1280) self.camera.set(4, 720)
class Main: def __init__(self): self.camera = cv2.VideoCapture(1, cv2.CAP_DSHOW) self.camera.set(3, 1280) self.camera.set(4, 720)
调用手部类,并将相关信息显示在实时画面中
def Gesture_recognition(self):
while True:
self.detector = HandDetector()
frame, img = self.camera.read()
img = self.detector.findHands(img)
lmList, bbox = self.detector.findPosition(img)
if lmList:
x_1, y_1 = bbox["bbox"][0], bbox["bbox"][1]
x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 = self.detector.fingersUp()
if (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1) and (x4 == 0 and x5 == 0 and x1 == 0):
cv2.putText(img, "2_TWO", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(0, 0, 255), 3)
elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1) and (x1 == 0 and x5 == 0):
cv2.putText(img, "3_THREE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(0, 0, 255), 3)
elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1) and (x1 == 0):
cv2.putText(img, "4_FOUR", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(0, 0, 255), 3)
elif x1 == 1 and x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1:
cv2.putText(img, "5_FIVE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(0, 0, 255), 3)
elif x2 == 1 and (x1 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0):
cv2.putText(img, "1_ONE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(0, 0, 255), 3)
elif x1 and (x2 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0):
cv2.putText(img, "GOOD!", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(0, 0, 255), 3)
cv2.imshow("camera", img)
if cv2.getWindowProperty('camera', cv2.WND_PROP_VISIBLE) < 1:
break
cv2.waitKey(1)def Gesture_recognition(self): while True: self.detector = HandDetector() frame, img = self.camera.read() img = self.detector.findHands(img) lmList, bbox = self.detector.findPosition(img) if lmList: x_1, y_1 = bbox["bbox"][0], bbox["bbox"][1] x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 = self.detector.fingersUp() if (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1) and (x4 == 0 and x5 == 0 and x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "2_TWO", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1) and (x1 == 0 and x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "3_THREE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1) and (x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "4_FOUR", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 == 1 and x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1: cv2.putText(img, "5_FIVE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x2 == 1 and (x1 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "1_ONE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 and (x2 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "GOOD!", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) cv2.imshow("camera", img) if cv2.getWindowProperty('camera', cv2.WND_PROP_VISIBLE) < 1: break cv2.waitKey(1)
复制def Gesture_recognition(self): while True: self.detector = HandDetector() frame, img = self.camera.read() img = self.detector.findHands(img) lmList, bbox = self.detector.findPosition(img) if lmList: x_1, y_1 = bbox["bbox"][0], bbox["bbox"][1] x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 = self.detector.fingersUp() if (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1) and (x4 == 0 and x5 == 0 and x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "2_TWO", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1) and (x1 == 0 and x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "3_THREE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1) and (x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "4_FOUR", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 == 1 and x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1: cv2.putText(img, "5_FIVE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x2 == 1 and (x1 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "1_ONE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 and (x2 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "GOOD!", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) cv2.imshow("camera", img) if cv2.getWindowProperty('camera', cv2.WND_PROP_VISIBLE) < 1: break cv2.waitKey(1)
def Gesture_recognition(self): while True: self.detector = HandDetector() frame, img = self.camera.read() img = self.detector.findHands(img) lmList, bbox = self.detector.findPosition(img) if lmList: x_1, y_1 = bbox["bbox"][0], bbox["bbox"][1] x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 = self.detector.fingersUp() if (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1) and (x4 == 0 and x5 == 0 and x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "2_TWO", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1) and (x1 == 0 and x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "3_THREE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1) and (x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "4_FOUR", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 == 1 and x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1: cv2.putText(img, "5_FIVE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x2 == 1 and (x1 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "1_ONE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 and (x2 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "GOOD!", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) cv2.imshow("camera", img) if cv2.getWindowProperty('camera', cv2.WND_PROP_VISIBLE) < 1: break cv2.waitKey(1)
def Gesture_recognition(self): while True: self.detector = HandDetector() frame, img = self.camera.read() img = self.detector.findHands(img) lmList, bbox = self.detector.findPosition(img) if lmList: x_1, y_1 = bbox["bbox"][0], bbox["bbox"][1] x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 = self.detector.fingersUp() if (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1) and (x4 == 0 and x5 == 0 and x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "2_TWO", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1) and (x1 == 0 and x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "3_THREE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1) and (x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "4_FOUR", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 == 1 and x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1: cv2.putText(img, "5_FIVE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x2 == 1 and (x1 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "1_ONE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 and (x2 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "GOOD!", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) cv2.imshow("camera", img) if cv2.getWindowProperty('camera', cv2.WND_PROP_VISIBLE) < 1: break cv2.waitKey(1)
程序入口:执行相关功能。
if __name__ == '__main__':
Solution = Main()
Solution.Gesture_recognition()if __name__ == '__main__': Solution = Main() Solution.Gesture_recognition()
复制if __name__ == '__main__': Solution = Main() Solution.Gesture_recognition()
if __name__ == '__main__': Solution = Main() Solution.Gesture_recognition()
if __name__ == '__main__': Solution = Main() Solution.Gesture_recognition()
完整代码展示 import cv2
import mediapipe as mp
class HandDetector:
"""
使用mediapipe库查找手。导出地标像素格式。添加了额外的功能。
如查找方式,许多手指向上或两个手指之间的距离。而且提供找到的手的边界框信息。
"""
def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, minTrackCon=0.5):
"""
:param mode: 在静态模式下,对每个图像进行检测
:param maxHands: 要检测的最大手数
:param detectionCon: 最小检测置信度
:param minTrackCon: 最小跟踪置信度
"""
self.mode = mode
self.maxHands = maxHands
self.modelComplex = False
self.detectionCon = detectionCon
self.minTrackCon = minTrackCon
# 初始化手部识别模型
self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands
self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(self.mode, self.maxHands, self.modelComplex,
self.detectionCon, self.minTrackCon)
self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils # 初始化绘图器
self.tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20] # 指尖列表
self.fingers = []
self.lmList = []
def findHands(self, img, draw=True):
"""
从图像(BRG)中找到手部。
:param img: 用于查找手的图像。
:param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。
:return: 带或不带图形的图像
"""
imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 将传入的图像由BGR模式转标准的Opencv模式——RGB模式,
self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB)
if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
if draw:
self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms,
self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS)
return img
def findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True):
"""
查找单手的地标并将其放入列表中像素格式。还可以返回手部周围的边界框。
:param img: 要查找的主图像
:param handNo: 如果检测到多只手,则为手部id
:param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。(默认绘制矩形框)
:return: 像素格式的手部关节位置列表;手部边界框
"""
xList = []
yList = []
bbox = []
bboxInfo = []
self.lmList = []
if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo]
for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark):
h, w, c = img.shape
px, py = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h)
xList.append(px)
yList.append(py)
self.lmList.append([px, py])
if draw:
cv2.circle(img, (px, py), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
xmin, xmax = min(xList), max(xList)
ymin, ymax = min(yList), max(yList)
boxW, boxH = xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin
bbox = xmin, ymin, boxW, boxH
cx, cy = bbox[0] + (bbox[2] // 2), \
bbox[1] + (bbox[3] // 2)
bboxInfo = {"id": id, "bbox": bbox, "center": (cx, cy)}
if draw:
cv2.rectangle(img, (bbox[0] - 20, bbox[1] - 20),
(bbox[0] + bbox[2] + 20, bbox[1] + bbox[3] + 20),
(0, 255, 0), 2)
return self.lmList, bboxInfo
def fingersUp(self):
"""
查找列表中打开并返回的手指数。会分别考虑左手和右手
:return:竖起手指的列表
"""
if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
myHandType = self.handType()
fingers = []
# Thumb
if myHandType == "Right":
if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] > self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]:
fingers.append(1)
else:
fingers.append(0)
else:
if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]:
fingers.append(1)
else:
fingers.append(0)
# 4 Fingers
for id in range(1, 5):
if self.lmList[self.tipIds[id]][1] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[id] - 2][1]:
fingers.append(1)
else:
fingers.append(0)
return fingers
def handType(self):
"""
检查传入的手部是左还是右
:return: "Right" 或 "Left"
"""
if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
if self.lmList[17][0] < self.lmList[5][0]:
return "Right"
else:
return "Left"
class Main:
def __init__(self):
self.camera = cv2.VideoCapture(1, cv2.CAP_DSHOW)
self.camera.set(3, 1280)
self.camera.set(4, 720)
def Gesture_recognition(self):
while True:
self.detector = HandDetector()
frame, img = self.camera.read()
img = self.detector.findHands(img)
lmList, bbox = self.detector.findPosition(img)
if lmList:
x_1, y_1 = bbox["bbox"][0], bbox["bbox"][1]
x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 = self.detector.fingersUp()
if (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1) and (x4 == 0 and x5 == 0 and x1 == 0):
cv2.putText(img, "2_TWO", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(0, 0, 255), 3)
elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1) and (x1 == 0 and x5 == 0):
cv2.putText(img, "3_THREE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(0, 0, 255), 3)
elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1) and (x1 == 0):
cv2.putText(img, "4_FOUR", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(0, 0, 255), 3)
elif x1 == 1 and x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1:
cv2.putText(img, "5_FIVE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(0, 0, 255), 3)
elif x2 == 1 and (x1 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0):
cv2.putText(img, "1_ONE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(0, 0, 255), 3)
elif x1 and (x2 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0):
cv2.putText(img, "GOOD!", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3,
(0, 0, 255), 3)
cv2.imshow("camera", img)
if cv2.getWindowProperty('camera', cv2.WND_PROP_VISIBLE) < 1:
break
cv2.waitKey(1)
# if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
# break
if __name__ == '__main__':
Solution = Main()
Solution.Gesture_recognition()import cv2 import mediapipe as mp class HandDetector: """ 使用mediapipe库查找手。导出地标像素格式。添加了额外的功能。 如查找方式,许多手指向上或两个手指之间的距离。而且提供找到的手的边界框信息。 """ def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, minTrackCon=0.5): """ :param mode: 在静态模式下,对每个图像进行检测 :param maxHands: 要检测的最大手数 :param detectionCon: 最小检测置信度 :param minTrackCon: 最小跟踪置信度 """ self.mode = mode self.maxHands = maxHands self.modelComplex = False self.detectionCon = detectionCon self.minTrackCon = minTrackCon # 初始化手部识别模型 self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(self.mode, self.maxHands, self.modelComplex, self.detectionCon, self.minTrackCon) self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils # 初始化绘图器 self.tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20] # 指尖列表 self.fingers = [] self.lmList = [] def findHands(self, img, draw=True): """ 从图像(BRG)中找到手部。 :param img: 用于查找手的图像。 :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。 :return: 带或不带图形的图像 """ imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 将传入的图像由BGR模式转标准的Opencv模式——RGB模式, self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB) if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if draw: self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms, self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS) return img def findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True): """ 查找单手的地标并将其放入列表中像素格式。还可以返回手部周围的边界框。 :param img: 要查找的主图像 :param handNo: 如果检测到多只手,则为手部id :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。(默认绘制矩形框) :return: 像素格式的手部关节位置列表;手部边界框 """ xList = [] yList = [] bbox = [] bboxInfo = [] self.lmList = [] if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo] for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark): h, w, c = img.shape px, py = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h) xList.append(px) yList.append(py) self.lmList.append([px, py]) if draw: cv2.circle(img, (px, py), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) xmin, xmax = min(xList), max(xList) ymin, ymax = min(yList), max(yList) boxW, boxH = xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin bbox = xmin, ymin, boxW, boxH cx, cy = bbox[0] + (bbox[2] // 2), \ bbox[1] + (bbox[3] // 2) bboxInfo = {"id": id, "bbox": bbox, "center": (cx, cy)} if draw: cv2.rectangle(img, (bbox[0] - 20, bbox[1] - 20), (bbox[0] + bbox[2] + 20, bbox[1] + bbox[3] + 20), (0, 255, 0), 2) return self.lmList, bboxInfo def fingersUp(self): """ 查找列表中打开并返回的手指数。会分别考虑左手和右手 :return:竖起手指的列表 """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHandType = self.handType() fingers = [] # Thumb if myHandType == "Right": if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] > self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) else: if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) # 4 Fingers for id in range(1, 5): if self.lmList[self.tipIds[id]][1] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[id] - 2][1]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) return fingers def handType(self): """ 检查传入的手部是左还是右 :return: "Right" 或 "Left" """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if self.lmList[17][0] < self.lmList[5][0]: return "Right" else: return "Left" class Main: def __init__(self): self.camera = cv2.VideoCapture(1, cv2.CAP_DSHOW) self.camera.set(3, 1280) self.camera.set(4, 720) def Gesture_recognition(self): while True: self.detector = HandDetector() frame, img = self.camera.read() img = self.detector.findHands(img) lmList, bbox = self.detector.findPosition(img) if lmList: x_1, y_1 = bbox["bbox"][0], bbox["bbox"][1] x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 = self.detector.fingersUp() if (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1) and (x4 == 0 and x5 == 0 and x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "2_TWO", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1) and (x1 == 0 and x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "3_THREE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1) and (x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "4_FOUR", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 == 1 and x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1: cv2.putText(img, "5_FIVE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x2 == 1 and (x1 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "1_ONE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 and (x2 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "GOOD!", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) cv2.imshow("camera", img) if cv2.getWindowProperty('camera', cv2.WND_PROP_VISIBLE) < 1: break cv2.waitKey(1) # if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"): # break if __name__ == '__main__': Solution = Main() Solution.Gesture_recognition()
复制import cv2 import mediapipe as mp class HandDetector: """ 使用mediapipe库查找手。导出地标像素格式。添加了额外的功能。 如查找方式,许多手指向上或两个手指之间的距离。而且提供找到的手的边界框信息。 """ def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, minTrackCon=0.5): """ :param mode: 在静态模式下,对每个图像进行检测 :param maxHands: 要检测的最大手数 :param detectionCon: 最小检测置信度 :param minTrackCon: 最小跟踪置信度 """ self.mode = mode self.maxHands = maxHands self.modelComplex = False self.detectionCon = detectionCon self.minTrackCon = minTrackCon # 初始化手部识别模型 self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(self.mode, self.maxHands, self.modelComplex, self.detectionCon, self.minTrackCon) self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils # 初始化绘图器 self.tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20] # 指尖列表 self.fingers = [] self.lmList = [] def findHands(self, img, draw=True): """ 从图像(BRG)中找到手部。 :param img: 用于查找手的图像。 :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。 :return: 带或不带图形的图像 """ imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 将传入的图像由BGR模式转标准的Opencv模式——RGB模式, self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB) if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if draw: self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms, self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS) return img def findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True): """ 查找单手的地标并将其放入列表中像素格式。还可以返回手部周围的边界框。 :param img: 要查找的主图像 :param handNo: 如果检测到多只手,则为手部id :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。(默认绘制矩形框) :return: 像素格式的手部关节位置列表;手部边界框 """ xList = [] yList = [] bbox = [] bboxInfo = [] self.lmList = [] if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo] for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark): h, w, c = img.shape px, py = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h) xList.append(px) yList.append(py) self.lmList.append([px, py]) if draw: cv2.circle(img, (px, py), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) xmin, xmax = min(xList), max(xList) ymin, ymax = min(yList), max(yList) boxW, boxH = xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin bbox = xmin, ymin, boxW, boxH cx, cy = bbox[0] + (bbox[2] // 2), \ bbox[1] + (bbox[3] // 2) bboxInfo = {"id": id, "bbox": bbox, "center": (cx, cy)} if draw: cv2.rectangle(img, (bbox[0] - 20, bbox[1] - 20), (bbox[0] + bbox[2] + 20, bbox[1] + bbox[3] + 20), (0, 255, 0), 2) return self.lmList, bboxInfo def fingersUp(self): """ 查找列表中打开并返回的手指数。会分别考虑左手和右手 :return:竖起手指的列表 """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHandType = self.handType() fingers = [] # Thumb if myHandType == "Right": if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] > self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) else: if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) # 4 Fingers for id in range(1, 5): if self.lmList[self.tipIds[id]][1] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[id] - 2][1]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) return fingers def handType(self): """ 检查传入的手部是左还是右 :return: "Right" 或 "Left" """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if self.lmList[17][0] < self.lmList[5][0]: return "Right" else: return "Left" class Main: def __init__(self): self.camera = cv2.VideoCapture(1, cv2.CAP_DSHOW) self.camera.set(3, 1280) self.camera.set(4, 720) def Gesture_recognition(self): while True: self.detector = HandDetector() frame, img = self.camera.read() img = self.detector.findHands(img) lmList, bbox = self.detector.findPosition(img) if lmList: x_1, y_1 = bbox["bbox"][0], bbox["bbox"][1] x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 = self.detector.fingersUp() if (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1) and (x4 == 0 and x5 == 0 and x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "2_TWO", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1) and (x1 == 0 and x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "3_THREE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1) and (x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "4_FOUR", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 == 1 and x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1: cv2.putText(img, "5_FIVE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x2 == 1 and (x1 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "1_ONE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 and (x2 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "GOOD!", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) cv2.imshow("camera", img) if cv2.getWindowProperty('camera', cv2.WND_PROP_VISIBLE) < 1: break cv2.waitKey(1) # if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"): # break if __name__ == '__main__': Solution = Main() Solution.Gesture_recognition()
import cv2 import mediapipe as mp class HandDetector: """ 使用mediapipe库查找手。导出地标像素格式。添加了额外的功能。 如查找方式,许多手指向上或两个手指之间的距离。而且提供找到的手的边界框信息。 """ def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, minTrackCon=0.5): """ :param mode: 在静态模式下,对每个图像进行检测 :param maxHands: 要检测的最大手数 :param detectionCon: 最小检测置信度 :param minTrackCon: 最小跟踪置信度 """ self.mode = mode self.maxHands = maxHands self.modelComplex = False self.detectionCon = detectionCon self.minTrackCon = minTrackCon # 初始化手部识别模型 self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(self.mode, self.maxHands, self.modelComplex, self.detectionCon, self.minTrackCon) self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils # 初始化绘图器 self.tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20] # 指尖列表 self.fingers = [] self.lmList = [] def findHands(self, img, draw=True): """ 从图像(BRG)中找到手部。 :param img: 用于查找手的图像。 :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。 :return: 带或不带图形的图像 """ imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 将传入的图像由BGR模式转标准的Opencv模式——RGB模式, self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB) if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if draw: self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms, self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS) return img def findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True): """ 查找单手的地标并将其放入列表中像素格式。还可以返回手部周围的边界框。 :param img: 要查找的主图像 :param handNo: 如果检测到多只手,则为手部id :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。(默认绘制矩形框) :return: 像素格式的手部关节位置列表;手部边界框 """ xList = [] yList = [] bbox = [] bboxInfo = [] self.lmList = [] if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo] for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark): h, w, c = img.shape px, py = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h) xList.append(px) yList.append(py) self.lmList.append([px, py]) if draw: cv2.circle(img, (px, py), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) xmin, xmax = min(xList), max(xList) ymin, ymax = min(yList), max(yList) boxW, boxH = xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin bbox = xmin, ymin, boxW, boxH cx, cy = bbox[0] + (bbox[2] // 2), \ bbox[1] + (bbox[3] // 2) bboxInfo = {"id": id, "bbox": bbox, "center": (cx, cy)} if draw: cv2.rectangle(img, (bbox[0] - 20, bbox[1] - 20), (bbox[0] + bbox[2] + 20, bbox[1] + bbox[3] + 20), (0, 255, 0), 2) return self.lmList, bboxInfo def fingersUp(self): """ 查找列表中打开并返回的手指数。会分别考虑左手和右手 :return:竖起手指的列表 """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHandType = self.handType() fingers = [] # Thumb if myHandType == "Right": if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] > self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) else: if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) # 4 Fingers for id in range(1, 5): if self.lmList[self.tipIds[id]][1] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[id] - 2][1]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) return fingers def handType(self): """ 检查传入的手部是左还是右 :return: "Right" 或 "Left" """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if self.lmList[17][0] < self.lmList[5][0]: return "Right" else: return "Left" class Main: def __init__(self): self.camera = cv2.VideoCapture(1, cv2.CAP_DSHOW) self.camera.set(3, 1280) self.camera.set(4, 720) def Gesture_recognition(self): while True: self.detector = HandDetector() frame, img = self.camera.read() img = self.detector.findHands(img) lmList, bbox = self.detector.findPosition(img) if lmList: x_1, y_1 = bbox["bbox"][0], bbox["bbox"][1] x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 = self.detector.fingersUp() if (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1) and (x4 == 0 and x5 == 0 and x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "2_TWO", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1) and (x1 == 0 and x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "3_THREE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1) and (x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "4_FOUR", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 == 1 and x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1: cv2.putText(img, "5_FIVE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x2 == 1 and (x1 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "1_ONE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 and (x2 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "GOOD!", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) cv2.imshow("camera", img) if cv2.getWindowProperty('camera', cv2.WND_PROP_VISIBLE) < 1: break cv2.waitKey(1) # if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"): # break if __name__ == '__main__': Solution = Main() Solution.Gesture_recognition()
import cv2 import mediapipe as mp class HandDetector: """ 使用mediapipe库查找手。导出地标像素格式。添加了额外的功能。 如查找方式,许多手指向上或两个手指之间的距离。而且提供找到的手的边界框信息。 """ def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, minTrackCon=0.5): """ :param mode: 在静态模式下,对每个图像进行检测 :param maxHands: 要检测的最大手数 :param detectionCon: 最小检测置信度 :param minTrackCon: 最小跟踪置信度 """ self.mode = mode self.maxHands = maxHands self.modelComplex = False self.detectionCon = detectionCon self.minTrackCon = minTrackCon # 初始化手部识别模型 self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands(self.mode, self.maxHands, self.modelComplex, self.detectionCon, self.minTrackCon) self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils # 初始化绘图器 self.tipIds = [4, 8, 12, 16, 20] # 指尖列表 self.fingers = [] self.lmList = [] def findHands(self, img, draw=True): """ 从图像(BRG)中找到手部。 :param img: 用于查找手的图像。 :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。 :return: 带或不带图形的图像 """ imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 将传入的图像由BGR模式转标准的Opencv模式——RGB模式, self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB) if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if draw: self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, handLms, self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS) return img def findPosition(self, img, handNo=0, draw=True): """ 查找单手的地标并将其放入列表中像素格式。还可以返回手部周围的边界框。 :param img: 要查找的主图像 :param handNo: 如果检测到多只手,则为手部id :param draw: 在图像上绘制输出的标志。(默认绘制矩形框) :return: 像素格式的手部关节位置列表;手部边界框 """ xList = [] yList = [] bbox = [] bboxInfo = [] self.lmList = [] if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo] for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark): h, w, c = img.shape px, py = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h) xList.append(px) yList.append(py) self.lmList.append([px, py]) if draw: cv2.circle(img, (px, py), 5, (255, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED) xmin, xmax = min(xList), max(xList) ymin, ymax = min(yList), max(yList) boxW, boxH = xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin bbox = xmin, ymin, boxW, boxH cx, cy = bbox[0] + (bbox[2] // 2), \ bbox[1] + (bbox[3] // 2) bboxInfo = {"id": id, "bbox": bbox, "center": (cx, cy)} if draw: cv2.rectangle(img, (bbox[0] - 20, bbox[1] - 20), (bbox[0] + bbox[2] + 20, bbox[1] + bbox[3] + 20), (0, 255, 0), 2) return self.lmList, bboxInfo def fingersUp(self): """ 查找列表中打开并返回的手指数。会分别考虑左手和右手 :return:竖起手指的列表 """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: myHandType = self.handType() fingers = [] # Thumb if myHandType == "Right": if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] > self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) else: if self.lmList[self.tipIds[0]][0] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[0] - 1][0]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) # 4 Fingers for id in range(1, 5): if self.lmList[self.tipIds[id]][1] < self.lmList[self.tipIds[id] - 2][1]: fingers.append(1) else: fingers.append(0) return fingers def handType(self): """ 检查传入的手部是左还是右 :return: "Right" 或 "Left" """ if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks: if self.lmList[17][0] < self.lmList[5][0]: return "Right" else: return "Left" class Main: def __init__(self): self.camera = cv2.VideoCapture(1, cv2.CAP_DSHOW) self.camera.set(3, 1280) self.camera.set(4, 720) def Gesture_recognition(self): while True: self.detector = HandDetector() frame, img = self.camera.read() img = self.detector.findHands(img) lmList, bbox = self.detector.findPosition(img) if lmList: x_1, y_1 = bbox["bbox"][0], bbox["bbox"][1] x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 = self.detector.fingersUp() if (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1) and (x4 == 0 and x5 == 0 and x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "2_TWO", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1) and (x1 == 0 and x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "3_THREE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif (x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1) and (x1 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "4_FOUR", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 == 1 and x2 == 1 and x3 == 1 and x4 == 1 and x5 == 1: cv2.putText(img, "5_FIVE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x2 == 1 and (x1 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "1_ONE", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) elif x1 and (x2 == 0, x3 == 0, x4 == 0, x5 == 0): cv2.putText(img, "GOOD!", (x_1, y_1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 0, 255), 3) cv2.imshow("camera", img) if cv2.getWindowProperty('camera', cv2.WND_PROP_VISIBLE) < 1: break cv2.waitKey(1) # if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"): # break if __name__ == '__main__': Solution = Main() Solution.Gesture_recognition()
复制








评论(0)
您还未登录,请登录后发表或查看评论