在Tensorflow中所有的数据都是使用tensor来描述的,不管是变量,常量,placeholder等都是一个tensor,tensor的中文翻译是张量,也就是我们在进行tensorflow编程的时候所有的输入输出都是一个tensor,这一点非常重要的。
下图是Tensorflow官方文档中的说明

从中可以看出我们使用python编程中
- s=483. 这样的简单变量,在Tensor中被描述为一个Rank=0的tensor
- v=[1.1,2.2,3.3]. 这种列表,在数学概念上是一种向量,而的tensorflow则被描述为Rank=1的tensor
- m=[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]],这种在数学上称之为矩阵的,在tensorflow中被描述为Rank=2的tensor
- tensor的Rank可以是等于3或者更高的数值
- Rank可以理解为tensor的维度,Rank越大Tensor就越复杂,所包含的信息量就越大
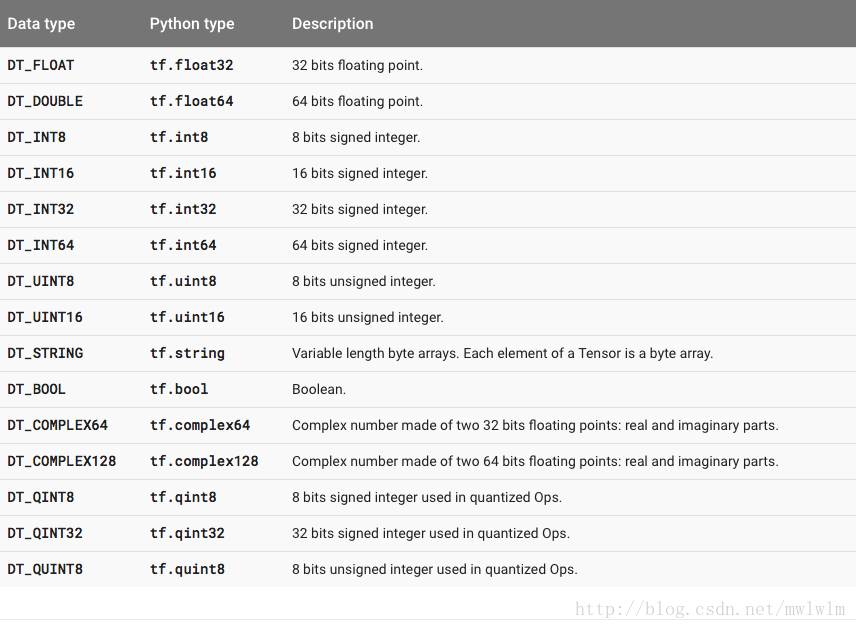
tensor中的每个元素可以被是各种数据类型,tensorflow中已经定义了15种基本的数据类型
定义rank=0的常量
node1 = tf.constant(3.0, tf.float32)
placeholder可以传递Rank=0或者Rank=1的输入参数
a=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
b=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
adder_node=a+b
print(sess.run(adder_node,{a:5,b:7}))
print(sess.run(adder_node,{a:[6,9],b:[9,7]}))
下面一段代码可以做为一个完整的练习,去理解tensor
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
node1 = tf.constant(3.0, tf.float32) # create a constant
node2 = tf.constant(4.0)
print(node1, node2) ##just print the node type
sess = tf.Session()
print(sess.run(node1), sess.run(node2)) ## print the node value
node3 = tf.add(node1, node2)
print("node3: ", node3)
print("sess.run node3:", sess.run(node3))
a=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
b=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
adder_node=a+b
print(sess.run(adder_node,{a:5,b:7}))
print(sess.run(adder_node,{a:[6,9],b:[9,7]}))
c=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
adder_and_triple= adder_node*c
print(sess.run(adder_and_triple,{a:[8,9],b:[1,6],c:3}))
执行完会输出如下内容:
3.0 4.0
node3: Tensor("Add:0", shape=(), dtype=float32)
sess.run node3: 7.0
可以看到执行如下这一句
print("node3: ", node3)
输出的结果是一个Tensor结构的描述
node3: Tensor("Add:0", shape=(), dtype=float32)
 从中可以看出我们使用python编程中
从中可以看出我们使用python编程中
 定义rank=0的常量
定义rank=0的常量





评论(0)
您还未登录,请登录后发表或查看评论