前面看spring源码时可以发现refresh()方法十分重要。在这个方法中会加载beanDefinition,同时创建bean对象。那么在springboot中有没有使用这个refresh()方法呢?
- 参考视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Bq4y1Q7GZ?p=6
- 通过视频的学习和自身的理解整理出的笔记。
一、前期准备
1.1 创建工程
创建springboot项目,springboot版本为2.5.0,引入spring-boot-starter-web依赖,pom文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.0</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
1.2 创建Controller
创建一个简单的Controller用于测试
@RestController
public class HelloController {
public void helloController() {
System.out.println("创建了");
}
@RequestMapping("hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}
二、探究过程
2.1 启动类
项目的运行只需要启动类中一行简单的代码,spring容器的创建就是通过SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args)这一行代码实现的。
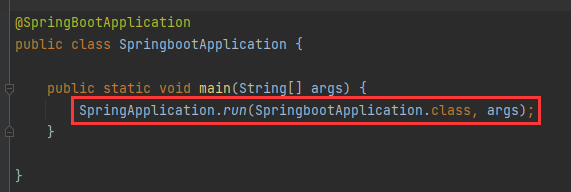
其实就是调用了静态的run方法,传入了启动类的字节码对象。
2.2 SpringApplication
run()方法
又调用了另一个run方法。
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class[]{primarySource}, args);
}
run()方法
方法的返回值类型为ConfigurableApplicationContext,ApplicationContext就是Spring的容器。
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
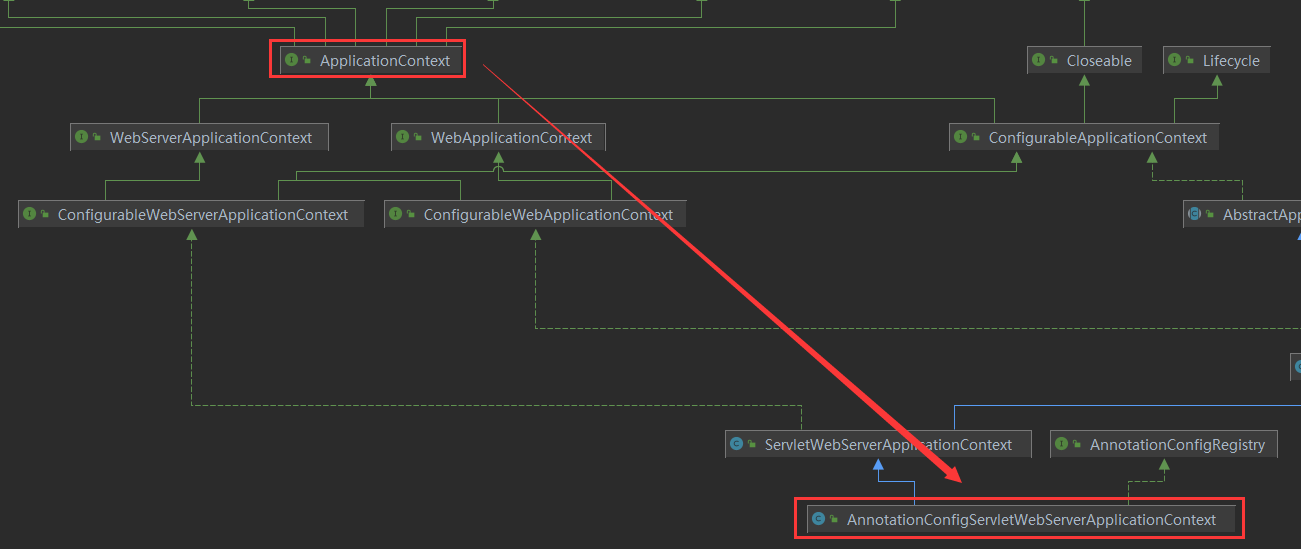
我们来看看ConfigurableApplicationContext继承结构
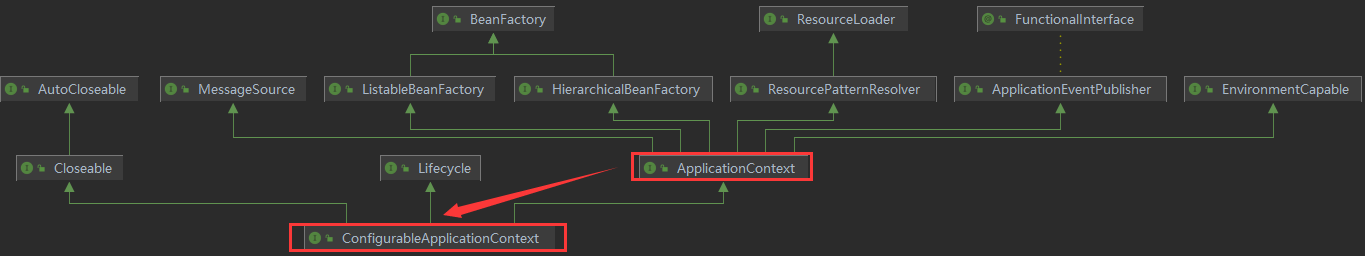
ConfigurableApplicationContext接口继承了ApplicationContext接口
下面我们通过debug进入run()方法中看看
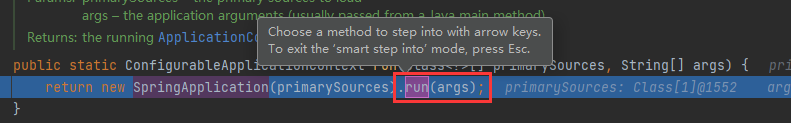
run()方法

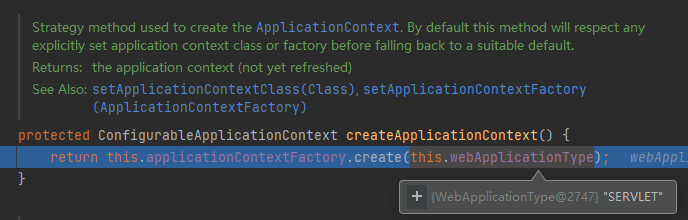
createApplicationContext()方法
容器工厂传入webApplication的类型,这个类型为Servlet应用。
Springboot可以做响应式的Web开发,这时webApplication的类型的类型就不是Servlet。
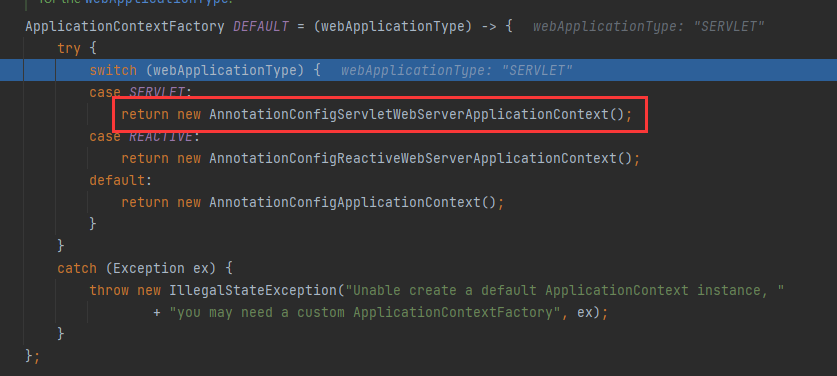
2.3 ApplicationContextFactory
这里是一个lambda表达式的写法,根据webApplicationType的类型返回对应的容器对象。
通过继承关系图可以看出,它的确是ApplicationContext
2.4 SpringApplication
run()方法,容器刷新前
看完了createApplicationContext()的过程,我们再次回到run()方法中,此时context已经创建完成。

我们观察一下context中都有些什么:
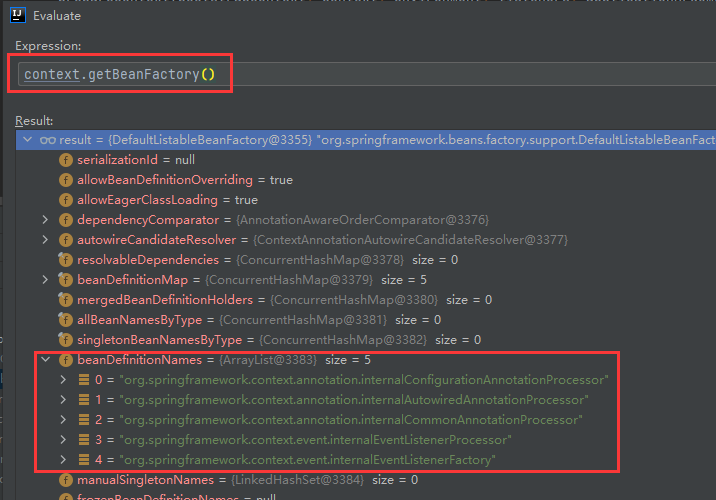
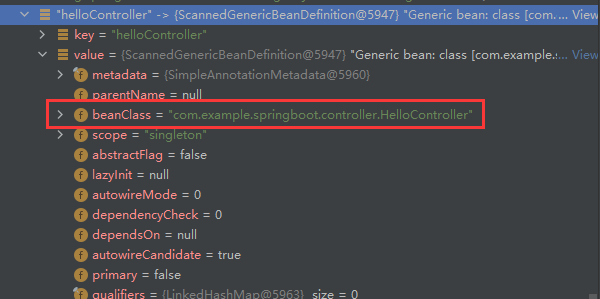
其中包含了bean工厂,bean工厂里有beanDefinitionNames和beanDefinitionMap。(与之前看的spring源码一样)
不过这里都是spring容器内置的beanDefinition对象,没有我们自定义的helloController,说明现在的容器还没有刷新。
我们现在获取不到HelloController的bean对象,当我们能获取到这个对象时,就说明容器刷新了。

run()方法,容器刷新后
继续往下运行,我们发现这行代码执行了好久,根据方法名称也可以看出它的功能就是刷新容器。
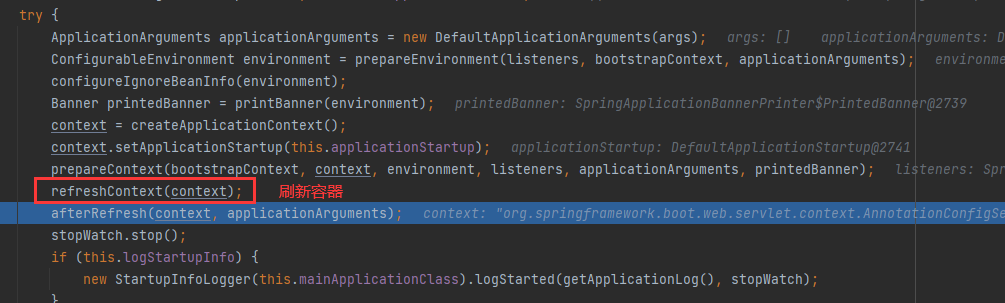
刷新后我们成功的获取到了bean对象。
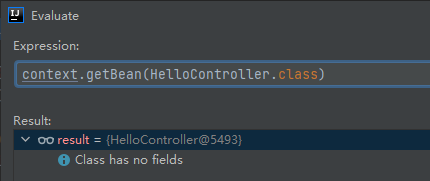
此时beanDefinitionMap中包含了138个对象,刷新之前只包含5个。我们可以在里面找到helloController(Hello的H变成了小写)
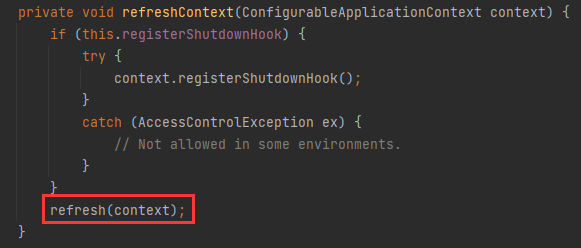
refreshContext()方法
下面我们看看refreshContext()方法,其中调用了refresh()方法。
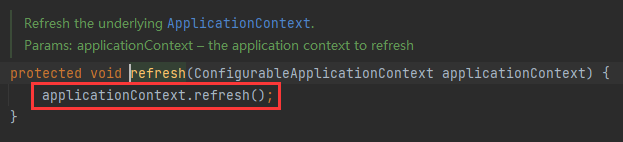
refresh()方法
refreshContext()方法中refresh(context)传入了容器对象,在这里调用了这个容器对象的refresh()方法。
后面暂时不往下看了。
2.5 结论
在启动类中调用SpringApplication的run方法时会根据容器的类型创建不同的容器对象,并调用容器的refresh方法。





评论(0)
您还未登录,请登录后发表或查看评论